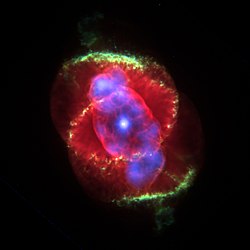
cats eye nebula
It has the combined magnitude of 8.1, with high surface brightness. Its small bright inner nebula subtends an average of 16.1 arcsec, with the outer prominent condensations about 25 arcsec. Deep images reveal an extended halo about 300 arcsec or 5 arcmin across, that was once ejected by the central progenitor star during its red giant phase. In the constellation draco.

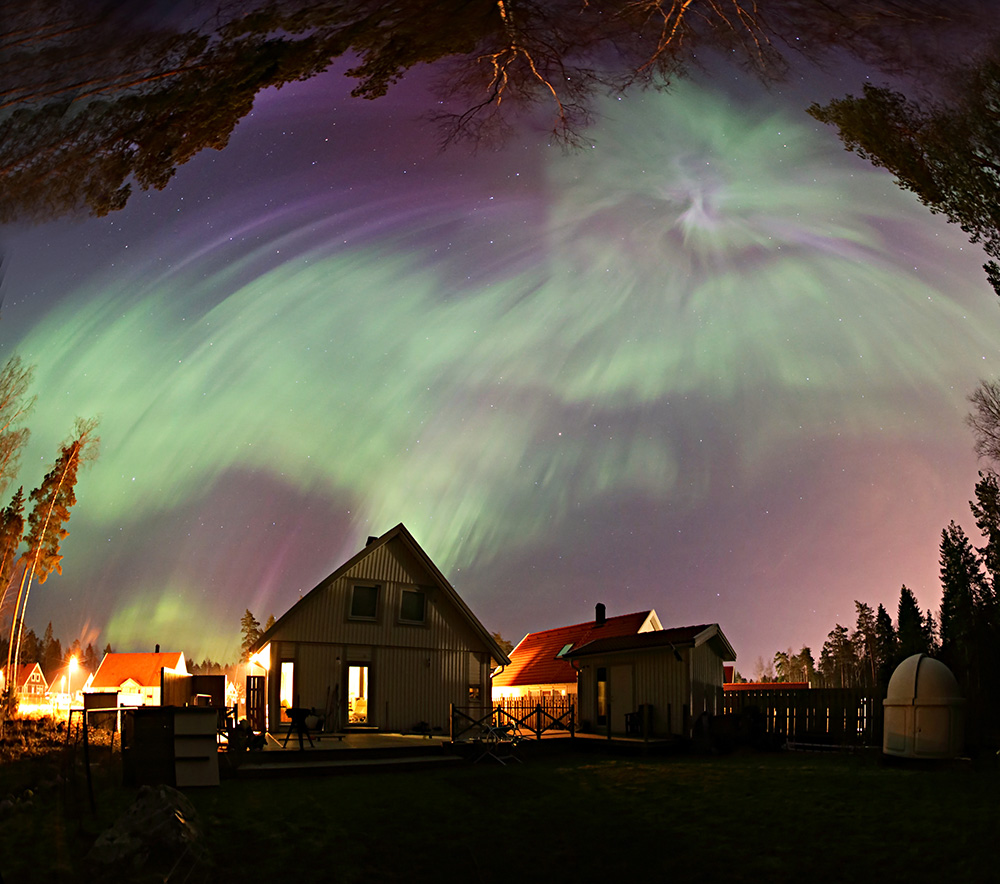
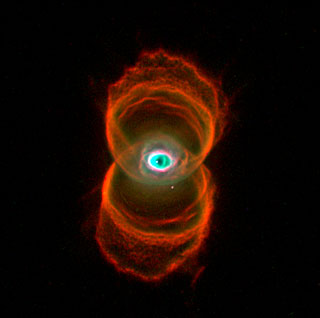
Ring Nebula
Messier 57 is located south of the bright star Vega , which forms the northwestern vertex of the Summer Triangle asterism.M57 is an example of the class of planetary nebulae known as bipolar nebulae, whose thick equatorial rings visibly extend the structure through its main axis of symmetry.

Dumbbell Nebula.
First nebula to ever be discovered by Charles messier.
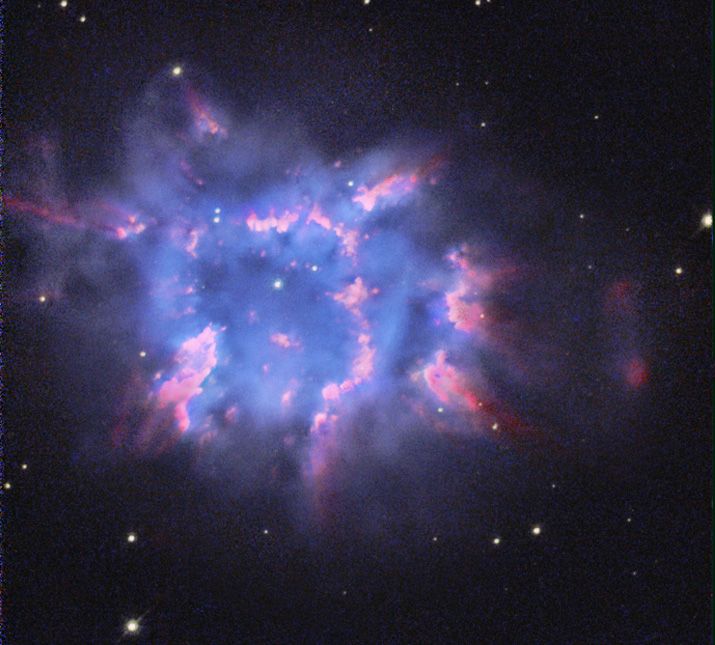
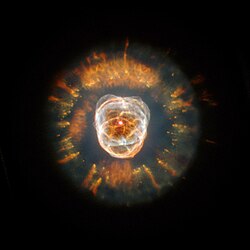
Hour glass nebula
8,000 LY away from earth. . It was discovered by Annie Jump Cannon and Margaret W. Mayall during their work on an extended Henry Draper Catalogue.
Wolf-Rayet Nebula
M1-67 is the youngest wind-nebula around a Wolf-Rayet star, calledWR124, in our Galaxy. In the constellaton cygnus.
The naked eye stars Gamma Velorum and Theta Muscae as well as the most massive start, R136a1 in 30 Doradus.Wolf–Rayet stars are extremely hot, with surface temperatures in the range of 30,000 K to around 200,000 K.
Planetary Nebula Hen 1357 or the Stingray Nebulas was photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope. It is located about 18,000 light-years from Earth and lies in the constellation Ara the Altar. This expanding cloud of gas was expelled from an aging star in the nebula’s centre.
NGC 6326 Located about 11,000 ly away from earth and in the constellation of Ara. This nebula is made of ejected material.
The Helix Nebula in the constellation of Aquarius lies about 700 light-years away, spanning about 0.8 Parsec or 2.5 light-years.
Eskimo Nebula
NGC 2392 lies more than 2,870 light-years away and is visible with a small Telescope in the constellation of Gemini. NGC 2392 WH IV-45 is included in the Astronomical League's Herschel 400 observing program.
The Necklace Nebula (PN G054.2-03.4) is a 12-trillion-mile-wide (2.0 light-year-wide) Planetary Nebula located about 15,000 light-years away in the northern constellation Sagitta. The Necklace Nebula is the exploded aftermath of a giant star that came too close to its Sun-like binary companion. The embedded bright knots are dense gas clumps in the ring.